Advance Maths Questions for SSC CGL CAT
Advance Maths Questions for SSC CGL CAT
Q1. Consider an obtuse-angled triangles with sides 8 cm, 15 cm and x cm. If x is an integer then how many such triangles exist?
A. 5
B. 21
C. 10
D. 15
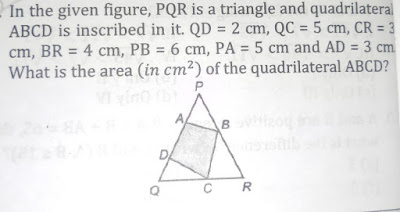
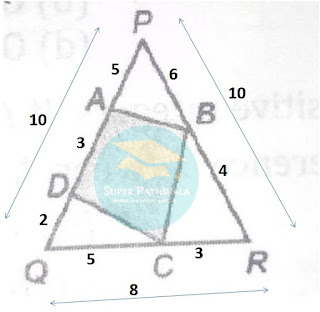
Q2. In the given figure , PQR is a triangle and quadrilateral ABCD is inscribed in it . QD = 2 cm , QC = 5 cm , CR = 3 cm , BR = 4 cm , PB = 6 cm , PA = 5 cm and AD = 3 cm . What is the area ( in cm² ) of the quadrilateral ABCD?
A. 17√21
B. 17/5
C. 17√21/5
D. √21/5
Q3. The quadratic equation x2 + mx + n = 0 has roots that are twice those of x2 + px + m = 0, and none of m, n and p is zero. What is the value of n/p?
(A) 2
(B) 16
(C) 4
(D) 8
Q4. Akash when going slower by 15 Km/hr, reaches late by 45 hours. If he goes faster by 10 Km/hr from his original speed, he reaches early by by 20 hours than the original time. Find the distance he covers.
आकाश जब 15 किमी/घंटा तक धीमी गति से चलता है, तो 45 घंटे देरी से पहुंचता है. यदि वह अपनी मूल गति से 10 किमी/घंटा तेजी से चलता है, तो वह मूल समय की तुलना में 20 घंटे जल्दी पहुंचता है. उसके द्वारा तय की जाने वाली दूरी ज्ञात कीजिये?
(A) 8750 Km/किमी
(B) 9750 Km/किमी
(C) 1000 Km/किमी
(D) 3750 Km/किमी
Q5. If x = √3/2 then find the value of √(1+x) - √(1-x)
(A) 1
(B) 0
(C) √3
(D) √2
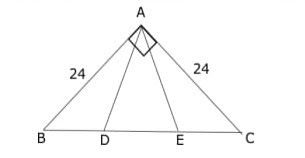
Q6. A right angled triangle with sides AB = AC = 24 , is cut into three parts of equal area as shown in the figure given below . Find the sum of perimeters of all the triangles in the figure.
(A) $144 + 40\sqrt{2} + 48\sqrt{5}$
(B) $144 + 80\sqrt{2} + 48\sqrt{5}$
(C) $72 + 40\sqrt{2} + 24\sqrt{5}$
(D) $72 + 40\sqrt{2} + 48\sqrt{5}$
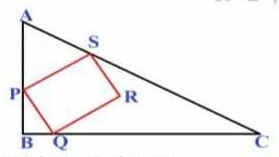
Q7. PQRS is a square inside an isosceles right angled triangle ABC , such that points P, Q and S lie on the sides AB, BC and AC, respectively. If BQ = 8cm, PB = 4cm and PR not parallel to BC, what is the area of the triangle outside the square?
PQRS एक वर्ग है जो समदविबाह समकोण त्रिभुज के अंदर बनाया गया है । जहाँ P, Q और S क्रमशः भुजा AB, BC और AC पर है । यदि BQ = 8cm, PB = 4cm और PR, BC के समांतर नही है तब वर्ग के बाहर त्रिभुज के भाग का क्षेत्रफल ज्ञात करे।
(A) 48 cm
(B) 96 cm
(C) 144 cm
(D) 64 cm
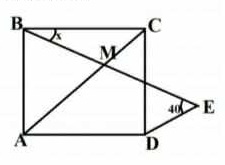
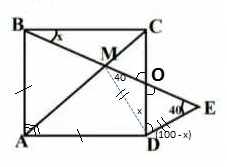
Q8. In the given fig . ABCD is a square, and BM = DE, calculate the value of x ?
दिए गए चित्र में , ABCD एक वर्ग है । और BM = DE तब x का मान ज्ञात करे।
(A) 40
(B) 20
(C) 25
(D) 30
1. Solution
If c is the side opposite the obtuse angle & hence the longest, it should satisfy the following two conditions:
a2 + b2 < c2 and c < a + b
If 15 is the longest side, then:
82 + x2 < 152
64 + x2 < 225
x2 < 161
x < 12.69
So, keeping with our other range, x could be 8, 9, 10, 11 or 12.
If we make x our longest side, we have:
82 + 152 < x2
64 + 225 < x2
289 < x2
17 < x
x could be 18, 19, 20, 21 or 22.
So 10 possible values for x.
Ans. C
2. Solution
Area of the ΔPQR = √(14×6×4×4) = 8√21
By using sin formula for area = 1/2abSinθ
Ratio of area of ΔAPB and ΔPQR = 5×6/10×10 = 30/100 = 3/10 = 3×8/10×8 = 24/80
Ratio of area of ΔQDC and ΔPQR = 5×2/10×8 = 10/80
Ratio of area of ΔBRC and ΔPQR = 3×4/10×8 = 12/80
So the ratio of area of □ABCD and ΔPQR = (80 - 24 - 10 - 12)/80 = 34/80
Now the area of 80 unit ΔPQR = 8√21
So 1 unit = 8√21/80 = √21/10
So the area of 34 unit □ABCD = 34×√21/10
= 17√21/5 Ans.
3. Solution
If the roots of x2 + px + m = 0 are α and β
then roots of x2 + mx + n = 0 will be 2α and 2β
then sum of roots of first equation (α + β) = -p
and multiplication of roots of first equation (α×β) = m
again sum of roots of second equation 2(α + β) = -m
and multiplication of roots of second equation 4α×β = n
from above equations 2(-p) = -m
=> 2p = m
and 4m = n
=> 8p = n
=>n/p = 8
4. Solution
Let the actual speed is "v" distance "d"
According to the conditions:
d/(v - 15) = d/v + 45
=> 15d/v(v -15) = 45 .....(i)
d/(v + 10) = d/v - 20
=> 10d/v(v +10) = 20 .....(ii)
divide (i) by (ii)
15(v + 10)/10(v - 15) = 45/20
(v + 10)/(v - 15) = 3/2
v = 65
from equation (i)
15d/65×50 = 45
d = 9750
So the total distance will be 9750 km
5. Solution
Give that x = √3/2
If z = √(1+x) - √(1-x)
z2 = (1+x) + (1-x) - 2√(1-x2)
z2 = 2 - 2√(1-3/4)
z2 = 2 - 2×1/2
z = 1
Ans: 1
6. Solution
Given that area of all traingle is same so base of all traingle will be equal because hieght is same
∴ BD = DE = EC = BC/3 = $8\sqrt{2}$ (∵ ∠BAC = 90°)
Given that ∠BAC = 90° and AB = AC = 24
∴ ∠ABC = ∠ACB = 45°
Now according to cosine rule in ΔACE
${AE}^2 = {24}^2 + {(8\sqrt{2})}^2 - 2×24×8\sqrt{2}\cos45°$
${AE}^2 = 320$
$AE = 8\sqrt{5}$
Same as $AD = 8\sqrt{5}$
Now sum of perimeter of all triangle
ΔABD + ΔADE + ΔAEC + ΔABE + ΔACD + ΔABC
= $144 + 80\sqrt{2} + 48\sqrt{5}$
Ans: B
7. Solution
Given that ΔABC is isosceles right angled triangle and BQ = 8cm PB = 4cm
∴ ∠BAC = ∠ACB = 45° (∵ ΔABC is isosceles right angled triangle)
$PQ = 4\sqrt{5}$ (by Pythagoras theorem)
Now using sine rule in ΔAPS
$\frac{PS}{\sin45°} = \frac{AS}{\sin∠APS}$
$\frac{PS}{1/\sqrt{2}} = \frac{AS}{\cos∠BPQ}$ (∵ ∠QPS = 90°)
$\frac{PS}{1/\sqrt{2}} = \frac{AS}{PB/PQ}$
$AS = 4\sqrt{2}$ (∵ PS = PQ and PB = 4)
Now using cosine rule in ΔAPS
${PS}^2 = {AP}^2 + {AS}^2 - 2×AP×AS×\cos45°$
$80 = {AP}^2 + 32 - 8AP$
${AP}^2 - 8AP - 48 = 0$
AP = 12 or -4 (-4 is not valid)
∴ AB = 12 +4 = 16
Now area of ΔABC = $\frac{1}{2}×16×16 = 128$
and area of square PQRS = ${(4\sqrt{5})}^2 = 80$
∴ The area of the triangle outside the square = 128 - 80 = 48
Ans: (A)
8. Solution
Given that ABCD is a square and BM = DE.
ΔBAM ≅ ΔDAM (by Side Angle Side postulate)
∴ BM = DM = DE (∵ BM = DE given)
Now in ΔDME
∠DME = ∠DEM = 40° (∵ DM = DE)
ΔMBC ≅ ΔMDC (by Side Side Side postulate)
∴ ∠MBC = ∠MDC = x
Now in ΔDME
∠ODE = 180 - 40 - 40 - x
∠ODE = 100 - x
in ΔBCO
∠BOC = (90 -x) (∵ ∠BCO = 90°)
∠BOC = ∠DOE (pairs of opposite angles)
Now in ΔDOE
(100 -x) + (90 -x) + 40 = 180
2x = 230 - 180
x = 25°
Ans: (C)
A. 5
B. 21
C. 10
D. 15
Q2. In the given figure , PQR is a triangle and quadrilateral ABCD is inscribed in it . QD = 2 cm , QC = 5 cm , CR = 3 cm , BR = 4 cm , PB = 6 cm , PA = 5 cm and AD = 3 cm . What is the area ( in cm² ) of the quadrilateral ABCD?
A. 17√21
B. 17/5
C. 17√21/5
D. √21/5
Q3. The quadratic equation x2 + mx + n = 0 has roots that are twice those of x2 + px + m = 0, and none of m, n and p is zero. What is the value of n/p?
(A) 2
(B) 16
(C) 4
(D) 8
Q4. Akash when going slower by 15 Km/hr, reaches late by 45 hours. If he goes faster by 10 Km/hr from his original speed, he reaches early by by 20 hours than the original time. Find the distance he covers.
आकाश जब 15 किमी/घंटा तक धीमी गति से चलता है, तो 45 घंटे देरी से पहुंचता है. यदि वह अपनी मूल गति से 10 किमी/घंटा तेजी से चलता है, तो वह मूल समय की तुलना में 20 घंटे जल्दी पहुंचता है. उसके द्वारा तय की जाने वाली दूरी ज्ञात कीजिये?
(A) 8750 Km/किमी
(B) 9750 Km/किमी
(C) 1000 Km/किमी
(D) 3750 Km/किमी
Q5. If x = √3/2 then find the value of √(1+x) - √(1-x)
(A) 1
(B) 0
(C) √3
(D) √2
Q6. A right angled triangle with sides AB = AC = 24 , is cut into three parts of equal area as shown in the figure given below . Find the sum of perimeters of all the triangles in the figure.
(A) $144 + 40\sqrt{2} + 48\sqrt{5}$
(B) $144 + 80\sqrt{2} + 48\sqrt{5}$
(C) $72 + 40\sqrt{2} + 24\sqrt{5}$
(D) $72 + 40\sqrt{2} + 48\sqrt{5}$
Q7. PQRS is a square inside an isosceles right angled triangle ABC , such that points P, Q and S lie on the sides AB, BC and AC, respectively. If BQ = 8cm, PB = 4cm and PR not parallel to BC, what is the area of the triangle outside the square?
PQRS एक वर्ग है जो समदविबाह समकोण त्रिभुज के अंदर बनाया गया है । जहाँ P, Q और S क्रमशः भुजा AB, BC और AC पर है । यदि BQ = 8cm, PB = 4cm और PR, BC के समांतर नही है तब वर्ग के बाहर त्रिभुज के भाग का क्षेत्रफल ज्ञात करे।
(A) 48 cm
(B) 96 cm
(C) 144 cm
(D) 64 cm
Q8. In the given fig . ABCD is a square, and BM = DE, calculate the value of x ?
दिए गए चित्र में , ABCD एक वर्ग है । और BM = DE तब x का मान ज्ञात करे।
(A) 40
(B) 20
(C) 25
(D) 30
Solution
1. Solution
If c is the side opposite the obtuse angle & hence the longest, it should satisfy the following two conditions:
a2 + b2 < c2 and c < a + b
If 15 is the longest side, then:
82 + x2 < 152
64 + x2 < 225
x2 < 161
x < 12.69
So, keeping with our other range, x could be 8, 9, 10, 11 or 12.
If we make x our longest side, we have:
82 + 152 < x2
64 + 225 < x2
289 < x2
17 < x
x could be 18, 19, 20, 21 or 22.
So 10 possible values for x.
Ans. C
2. Solution
Area of the ΔPQR = √(14×6×4×4) = 8√21
By using sin formula for area = 1/2abSinθ
Ratio of area of ΔAPB and ΔPQR = 5×6/10×10 = 30/100 = 3/10 = 3×8/10×8 = 24/80
Ratio of area of ΔQDC and ΔPQR = 5×2/10×8 = 10/80
Ratio of area of ΔBRC and ΔPQR = 3×4/10×8 = 12/80
So the ratio of area of □ABCD and ΔPQR = (80 - 24 - 10 - 12)/80 = 34/80
Now the area of 80 unit ΔPQR = 8√21
So 1 unit = 8√21/80 = √21/10
So the area of 34 unit □ABCD = 34×√21/10
= 17√21/5 Ans.
3. Solution
If the roots of x2 + px + m = 0 are α and β
then roots of x2 + mx + n = 0 will be 2α and 2β
then sum of roots of first equation (α + β) = -p
and multiplication of roots of first equation (α×β) = m
again sum of roots of second equation 2(α + β) = -m
and multiplication of roots of second equation 4α×β = n
from above equations 2(-p) = -m
=> 2p = m
and 4m = n
=> 8p = n
=>n/p = 8
4. Solution
Let the actual speed is "v" distance "d"
According to the conditions:
d/(v - 15) = d/v + 45
=> 15d/v(v -15) = 45 .....(i)
d/(v + 10) = d/v - 20
=> 10d/v(v +10) = 20 .....(ii)
divide (i) by (ii)
15(v + 10)/10(v - 15) = 45/20
(v + 10)/(v - 15) = 3/2
v = 65
from equation (i)
15d/65×50 = 45
d = 9750
So the total distance will be 9750 km
5. Solution
Give that x = √3/2
If z = √(1+x) - √(1-x)
z2 = (1+x) + (1-x) - 2√(1-x2)
z2 = 2 - 2√(1-3/4)
z2 = 2 - 2×1/2
z = 1
Ans: 1
6. Solution
Given that area of all traingle is same so base of all traingle will be equal because hieght is same
∴ BD = DE = EC = BC/3 = $8\sqrt{2}$ (∵ ∠BAC = 90°)
Given that ∠BAC = 90° and AB = AC = 24
∴ ∠ABC = ∠ACB = 45°
Now according to cosine rule in ΔACE
${AE}^2 = {24}^2 + {(8\sqrt{2})}^2 - 2×24×8\sqrt{2}\cos45°$
${AE}^2 = 320$
$AE = 8\sqrt{5}$
Same as $AD = 8\sqrt{5}$
Now sum of perimeter of all triangle
ΔABD + ΔADE + ΔAEC + ΔABE + ΔACD + ΔABC
= $144 + 80\sqrt{2} + 48\sqrt{5}$
Ans: B
7. Solution
Given that ΔABC is isosceles right angled triangle and BQ = 8cm PB = 4cm
∴ ∠BAC = ∠ACB = 45° (∵ ΔABC is isosceles right angled triangle)
$PQ = 4\sqrt{5}$ (by Pythagoras theorem)
Now using sine rule in ΔAPS
$\frac{PS}{\sin45°} = \frac{AS}{\sin∠APS}$
$\frac{PS}{1/\sqrt{2}} = \frac{AS}{\cos∠BPQ}$ (∵ ∠QPS = 90°)
$\frac{PS}{1/\sqrt{2}} = \frac{AS}{PB/PQ}$
$AS = 4\sqrt{2}$ (∵ PS = PQ and PB = 4)
Now using cosine rule in ΔAPS
${PS}^2 = {AP}^2 + {AS}^2 - 2×AP×AS×\cos45°$
$80 = {AP}^2 + 32 - 8AP$
${AP}^2 - 8AP - 48 = 0$
AP = 12 or -4 (-4 is not valid)
∴ AB = 12 +4 = 16
Now area of ΔABC = $\frac{1}{2}×16×16 = 128$
and area of square PQRS = ${(4\sqrt{5})}^2 = 80$
∴ The area of the triangle outside the square = 128 - 80 = 48
Ans: (A)
8. Solution
Given that ABCD is a square and BM = DE.
ΔBAM ≅ ΔDAM (by Side Angle Side postulate)
∴ BM = DM = DE (∵ BM = DE given)
Now in ΔDME
∠DME = ∠DEM = 40° (∵ DM = DE)
ΔMBC ≅ ΔMDC (by Side Side Side postulate)
∴ ∠MBC = ∠MDC = x
Now in ΔDME
∠ODE = 180 - 40 - 40 - x
∠ODE = 100 - x
in ΔBCO
∠BOC = (90 -x) (∵ ∠BCO = 90°)
∠BOC = ∠DOE (pairs of opposite angles)
Now in ΔDOE
(100 -x) + (90 -x) + 40 = 180
2x = 230 - 180
x = 25°
Ans: (C)
Categories
- Ancient History Quiz
- Medieval History Quiz
- Modern History Quiz
- Indian Polity Quiz
- Physical Geography Quiz
- World Geography Quiz
- Geography of India Quiz
- Indian Economy Quiz
- Indian Arts and Culture Quiz
- Physics Quiz
- Chemistry Quiz
- Biology Quiz
- Computer Basics Quiz
- Sports Quiz
- Samanya Hindi Quiz
- Miscellaneous Quiz
Tags
SSC Quiz Study Notes The Hindu Vocab